 |
| January 17, 2023 | Volume 19 Issue 02 |
Mechanical News & Products
Designfax weekly eMagazine
Archives
Partners
Manufacturing Center
Product Spotlight
Modern Applications News
Metalworking Ideas For
Today's Job Shops
Tooling and Production
Strategies for large
metalworking plants
Engineer's Toolbox: How to design the optimum hinge
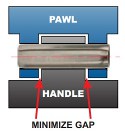 Although many pin styles are available, Coiled Spring Pins are particularly well suited for
use in both friction- and free-fit hinges. To achieve optimum long-term hinge performance,
designers should observe these helpful design guidelines from SPIROL.
Although many pin styles are available, Coiled Spring Pins are particularly well suited for
use in both friction- and free-fit hinges. To achieve optimum long-term hinge performance,
designers should observe these helpful design guidelines from SPIROL.
Read the full article.
Innovative new robo welding gun
 Comau's newest N-WG welding gun is designed for high-speed spot welding for traditional, hybrid, and electric vehicles, in addition to general industry sectors. It features a patented, single-body architecture that enables rapid reconfiguration between welding types and forces, and it delivers consistent performance across a broad range of applications, including steel and (soon) aluminum welding. It supports both X and C standard gun configurations, has fast arm exchange, and universal mounting options. It is fully compatible with major robot brands and represents a significant advancement in spot welding performance and cost efficiency.
Comau's newest N-WG welding gun is designed for high-speed spot welding for traditional, hybrid, and electric vehicles, in addition to general industry sectors. It features a patented, single-body architecture that enables rapid reconfiguration between welding types and forces, and it delivers consistent performance across a broad range of applications, including steel and (soon) aluminum welding. It supports both X and C standard gun configurations, has fast arm exchange, and universal mounting options. It is fully compatible with major robot brands and represents a significant advancement in spot welding performance and cost efficiency.
Learn more.
What's a SLIC Pin®? Pin and cotter all in one!
 The SLIC Pin (Self-Locking Implanted Cotter Pin) from Pivot Point is a pin and cotter all in one. This one-piece locking clevis pin is cost saving, fast, and secure. It functions as a quick locking pin wherever you need a fast-lock function. It features a spring-loaded plunger that functions as an easy insertion ramp. This revolutionary fastening pin is very popular and used successfully in a wide range of applications.
The SLIC Pin (Self-Locking Implanted Cotter Pin) from Pivot Point is a pin and cotter all in one. This one-piece locking clevis pin is cost saving, fast, and secure. It functions as a quick locking pin wherever you need a fast-lock function. It features a spring-loaded plunger that functions as an easy insertion ramp. This revolutionary fastening pin is very popular and used successfully in a wide range of applications.
Learn more.
Engineering challenge: Which 3D-printed parts will fade?
 How does prolonged exposure to intense UV light impact 3D-printed plastics? Will they fade? This is what Xometry's Director of Application Engineering, Greg Paulsen, set to find out. In this video, Paulsen performs comprehensive tests on samples manufactured using various additive processes, including FDM, SLS, SLA, PolyJet, DLS, and LSPc, to determine their UV resistance. Very informative. Some results may surprise you.
How does prolonged exposure to intense UV light impact 3D-printed plastics? Will they fade? This is what Xometry's Director of Application Engineering, Greg Paulsen, set to find out. In this video, Paulsen performs comprehensive tests on samples manufactured using various additive processes, including FDM, SLS, SLA, PolyJet, DLS, and LSPc, to determine their UV resistance. Very informative. Some results may surprise you.
View the video.
Copper filament for 3D printing
 Virtual Foundry, the company that brought us 3D-printable lunar regolith simulant, says its popular Copper Filamet™ (not a typo) is "back in stock and ready for your next project." This material is compatible with any open-architecture FDM/FFF 3D printer. After sintering, final parts are 100% pure copper. Also available as pellets. The company says this is one of the easiest materials to print and sinter. New Porcelain Filamet™ available too.
Virtual Foundry, the company that brought us 3D-printable lunar regolith simulant, says its popular Copper Filamet™ (not a typo) is "back in stock and ready for your next project." This material is compatible with any open-architecture FDM/FFF 3D printer. After sintering, final parts are 100% pure copper. Also available as pellets. The company says this is one of the easiest materials to print and sinter. New Porcelain Filamet™ available too.
Learn more and get all the specs.
Copper foam -- so many advantages
 Copper foam from Goodfellow combines the outstanding thermal conductivity of copper with the structural benefits of a metal foam. These features are of particular interest to design engineers working in the fields of medical products and devices, defense systems and manned flight, power generation, and the manufacture of semiconductor devices. This product has a true skeletal structure with no voids, inclusions, or entrapments. A perennial favorite of Designfax readers.
Copper foam from Goodfellow combines the outstanding thermal conductivity of copper with the structural benefits of a metal foam. These features are of particular interest to design engineers working in the fields of medical products and devices, defense systems and manned flight, power generation, and the manufacture of semiconductor devices. This product has a true skeletal structure with no voids, inclusions, or entrapments. A perennial favorite of Designfax readers.
Learn more.
Full-color 3D-printing Design Guide from Xometry
 With Xometry's PolyJet 3D-printing service, you can order full-color 3D prints easily. Their no-cost design guide will help you learn about different aspects of 3D printing colorful parts, how to create and add color to your models, and best practices to keep in mind when printing in full color. Learn how to take full advantage of the 600,000 unique colors available in this flexible additive process.
With Xometry's PolyJet 3D-printing service, you can order full-color 3D prints easily. Their no-cost design guide will help you learn about different aspects of 3D printing colorful parts, how to create and add color to your models, and best practices to keep in mind when printing in full color. Learn how to take full advantage of the 600,000 unique colors available in this flexible additive process.
Get the Xometry guide.
Tech Tip: How to create high-quality STL files for 3D prints
 Have you ever 3D printed a part that had flat spots or faceted surfaces where smooth curves were supposed to be? You are not alone, and it's not your 3D printer's fault. According to Markforged, the culprit is likely a lack of resolution in the STL file used to create the part.
Have you ever 3D printed a part that had flat spots or faceted surfaces where smooth curves were supposed to be? You are not alone, and it's not your 3D printer's fault. According to Markforged, the culprit is likely a lack of resolution in the STL file used to create the part.
Read this detailed and informative Markforged blog.
Test your knowledge: High-temp adhesives
 Put your knowledge to the test by trying to answer these key questions on how to choose the right high-temperature-resistant adhesive. The technical experts from Master Bond cover critical information necessary for the selection process, including questions on glass transition temperature and service temperature range. Some of the answers may surprise even the savviest of engineers.
Put your knowledge to the test by trying to answer these key questions on how to choose the right high-temperature-resistant adhesive. The technical experts from Master Bond cover critical information necessary for the selection process, including questions on glass transition temperature and service temperature range. Some of the answers may surprise even the savviest of engineers.
Take the quiz.
Engineer's Toolbox: How to pin a shaft and hub assembly properly
 One of the primary benefits of using a coiled spring pin to affix a hub or gear to a shaft is the coiled pin's ability to prevent hole damage. Another is the coiled pin absorbs wider hole tolerances than any other press-fit pin. This translates to lower total manufacturing costs of the assembly. However, there are a few design guidelines that must be adhered to in order to achieve the maximum strength of the pinned system and prevent damage to the assembly.
One of the primary benefits of using a coiled spring pin to affix a hub or gear to a shaft is the coiled pin's ability to prevent hole damage. Another is the coiled pin absorbs wider hole tolerances than any other press-fit pin. This translates to lower total manufacturing costs of the assembly. However, there are a few design guidelines that must be adhered to in order to achieve the maximum strength of the pinned system and prevent damage to the assembly.
Read this very informative SPIROL article.
What's new in Creo Parametric 11.0?
 Creo Parametric 11.0 is packed with productivity-enhancing updates, and sometimes the smallest changes make the biggest impact in your daily workflows. Mark Potrzebowski, Technical Training Engineer, Rand 3D, runs through the newest functionality -- from improved surface modeling tools to smarter file management and model tree navigation. Videos provide extra instruction.
Creo Parametric 11.0 is packed with productivity-enhancing updates, and sometimes the smallest changes make the biggest impact in your daily workflows. Mark Potrzebowski, Technical Training Engineer, Rand 3D, runs through the newest functionality -- from improved surface modeling tools to smarter file management and model tree navigation. Videos provide extra instruction.
Read the full article.
What's so special about wave springs?
 Don't settle for ordinary springs. Opt for Rotor Clip wave springs. A wave spring is a type of flat wire compression spring characterized by its unique waveform-like structure. Unlike traditional coil springs, wave springs offer an innovative solution to complex engineering challenges, producing forces from bending, not torsion. Their standout feature lies in their ability to compress and expand efficiently while occupying up to 50% less axial space than traditional compression springs. Experience the difference Rotor Clip wave springs can make in your applications today!
Don't settle for ordinary springs. Opt for Rotor Clip wave springs. A wave spring is a type of flat wire compression spring characterized by its unique waveform-like structure. Unlike traditional coil springs, wave springs offer an innovative solution to complex engineering challenges, producing forces from bending, not torsion. Their standout feature lies in their ability to compress and expand efficiently while occupying up to 50% less axial space than traditional compression springs. Experience the difference Rotor Clip wave springs can make in your applications today!
View the video.
New Standard Parts Handbook from JW Winco
 JW Winco's printed Standard Parts Handbook is a comprehensive 2,184-page reference that supports designers and engineers with the largest selection of standard parts categorized into three main groups: operating, clamping, and machine parts. More than 75,000 standard parts can be found in this valuable resource, including toggle clamps, shaft collars, concealed multiple-joint hinges, and hygienically designed components.
JW Winco's printed Standard Parts Handbook is a comprehensive 2,184-page reference that supports designers and engineers with the largest selection of standard parts categorized into three main groups: operating, clamping, and machine parts. More than 75,000 standard parts can be found in this valuable resource, including toggle clamps, shaft collars, concealed multiple-joint hinges, and hygienically designed components.
Get your Standard Parts Handbook today.
Looking to save space in your designs?
 Watch Smalley's quick explainer video to see how engineer Frank improved his product designs by switching from traditional coil springs to compact, efficient wave springs. Tasked with making his products smaller while keeping costs down, Frank found wave springs were the perfect solution.
Watch Smalley's quick explainer video to see how engineer Frank improved his product designs by switching from traditional coil springs to compact, efficient wave springs. Tasked with making his products smaller while keeping costs down, Frank found wave springs were the perfect solution.
View the video.
Top die casting design tips
 You can improve the design and cost of your die cast parts with these top tips from Xometry's Joel Schadegg. Topics include: Fillets and Radii, Wall Thicknesses, Ribs and Metal Savers, Holes and Windows, Parting Lines, and more. Follow these recommendations so you have the highest chance of success with your project.
You can improve the design and cost of your die cast parts with these top tips from Xometry's Joel Schadegg. Topics include: Fillets and Radii, Wall Thicknesses, Ribs and Metal Savers, Holes and Windows, Parting Lines, and more. Follow these recommendations so you have the highest chance of success with your project.
Read the full Xometry article.
Researchers shrink camera to the size of a salt grain
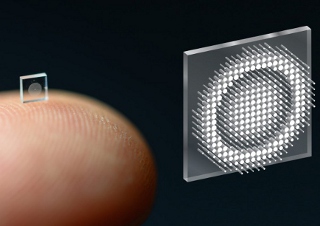
Researchers at Princeton University and the University of Washington have developed an ultracompact camera the size of a coarse grain of salt. The system relies on a technology called a metasurface, which is studded with 1.6 million cylindrical posts and can be produced much like a computer chip. [Image courtesy of the researchers]
By Molly Sharlach, Princeton University
Micro-sized cameras have great potential to spot problems in the human body and enable sensing for super-small robots, but past approaches captured fuzzy, distorted images with limited fields of view.
Now, researchers at Princeton University and the University of Washington have overcome these obstacles with an ultracompact camera the size of a coarse grain of salt. The new system can produce crisp, full-color images on par with a conventional compound camera lens 500,000 times larger in volume, the researchers reported in a paper published Nov. 29, 2021, in Nature Communications.
Enabled by a joint design of the camera's hardware and computational processing, the system could enable minimally invasive endoscopy with medical robots to diagnose and treat diseases, and improve imaging for other robots with size and weight constraints. Arrays of thousands of such cameras could be used for full-scene sensing, turning surfaces into cameras.
While a traditional camera uses a series of curved glass or plastic lenses to bend light rays into focus, the new optical system relies on a technology called a metasurface, which can be produced much like a computer chip. Just half a millimeter wide, the metasurface is studded with 1.6 million cylindrical posts, each roughly the size of the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV).
Each post has a unique geometry, and functions like an optical antenna. Varying the design of each post is necessary to correctly shape the entire optical wavefront. With the help of machine learning-based algorithms, the posts' interactions with light combine to produce the highest-quality images and widest field of view for a full-color metasurface camera developed to date.
A key innovation in the camera's creation was the integrated design of the optical surface and the signal processing algorithms that produce the image. This boosted the camera's performance in natural light conditions, in contrast to previous metasurface cameras that required the pure laser light of a laboratory or other ideal conditions to produce high-quality images, said Felix Heide, the study's senior author and an assistant professor of computer science at Princeton.
The researchers compared images produced with their system to the results of previous metasurface cameras, as well as images captured by a conventional compound optic that uses a series of six refractive lenses. Aside from a bit of blurring at the edges of the frame, the nano-sized camera's images were comparable to those of the traditional lens setup, which is more than 500,000 times larger in volume.
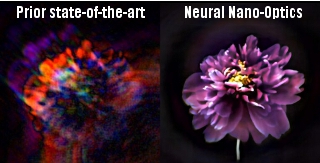
Previous micro-sized cameras (left) captured fuzzy, distorted images with limited fields of view. A new system called neural nano-optics (right) can produce crisp, full-color images on par with a conventional compound camera lens. [Image courtesy of the researchers]
Other ultracompact metasurface lenses have suffered from major image distortions, small fields of view, and limited ability to capture the full spectrum of visible light -- referred to as RGB imaging because it combines red, green, and blue to produce different hues.
"The significance of the published work is completing the Herculean task to jointly design the size, shape, and location of the metasurface's million features and the parameters of the post-detection processing to achieve the desired imaging performance," said Joseph Mait, a consultant at Mait-Optik and a former senior researcher and chief scientist at the U.S. Army Research Laboratory.
Heide and his colleagues are now working to add more computational abilities to the camera itself. Beyond optimizing image quality, they would like to add capabilities for object detection and other sensing modalities relevant for medicine and robotics
Published February 2022
Rate this article
View our terms of use and privacy policy

