 |
| July 11, 2017 | Volume 13 Issue 26 |
Materials News & Products
Designfax weekly eMagazine
Archives
Partners
Manufacturing Center
Product Spotlight
Modern Applications News
Metalworking Ideas For
Today's Job Shops
Tooling and Production
Strategies for large
metalworking plants
Engineering challenge: Which 3D-printed parts will fade?
 How does prolonged exposure to intense UV light impact 3D-printed plastics? Will they fade? This is what Xometry's Director of Application Engineering, Greg Paulsen, set to find out. In this video, Paulsen performs comprehensive tests on samples manufactured using various additive processes, including FDM, SLS, SLA, PolyJet, DLS, and LSPc, to determine their UV resistance. Very informative. Some results may surprise you.
How does prolonged exposure to intense UV light impact 3D-printed plastics? Will they fade? This is what Xometry's Director of Application Engineering, Greg Paulsen, set to find out. In this video, Paulsen performs comprehensive tests on samples manufactured using various additive processes, including FDM, SLS, SLA, PolyJet, DLS, and LSPc, to determine their UV resistance. Very informative. Some results may surprise you.
View the video.
Copper filament for 3D printing
 Virtual Foundry, the company that brought us 3D-printable lunar regolith simulant, says its popular Copper Filamet™ (not a typo) is "back in stock and ready for your next project." This material is compatible with any open-architecture FDM/FFF 3D printer. After sintering, final parts are 100% pure copper. Also available as pellets. The company says this is one of the easiest materials to print and sinter. New Porcelain Filamet™ available too.
Virtual Foundry, the company that brought us 3D-printable lunar regolith simulant, says its popular Copper Filamet™ (not a typo) is "back in stock and ready for your next project." This material is compatible with any open-architecture FDM/FFF 3D printer. After sintering, final parts are 100% pure copper. Also available as pellets. The company says this is one of the easiest materials to print and sinter. New Porcelain Filamet™ available too.
Learn more and get all the specs.
Copper foam -- so many advantages
 Copper foam from Goodfellow combines the outstanding thermal conductivity of copper with the structural benefits of a metal foam. These features are of particular interest to design engineers working in the fields of medical products and devices, defense systems and manned flight, power generation, and the manufacture of semiconductor devices. This product has a true skeletal structure with no voids, inclusions, or entrapments. A perennial favorite of Designfax readers.
Copper foam from Goodfellow combines the outstanding thermal conductivity of copper with the structural benefits of a metal foam. These features are of particular interest to design engineers working in the fields of medical products and devices, defense systems and manned flight, power generation, and the manufacture of semiconductor devices. This product has a true skeletal structure with no voids, inclusions, or entrapments. A perennial favorite of Designfax readers.
Learn more.
When glass or plastic can't cut it: Transparent ceramics solve critical design challenges
 Complex designs are still possible when grinding and polishing Fused Silica or Sapphire. Ceramic properties such as wear, abrasion resistance, and strength of these optical materials can be a designer's dream solution when high temperatures or severe environments rule out standard optical glass or plastic. INSACO is a machine shop specializing in ultra-hard and extreme materials.
Complex designs are still possible when grinding and polishing Fused Silica or Sapphire. Ceramic properties such as wear, abrasion resistance, and strength of these optical materials can be a designer's dream solution when high temperatures or severe environments rule out standard optical glass or plastic. INSACO is a machine shop specializing in ultra-hard and extreme materials.
→ Contact Jackson Evans, Sales Engineer at INSACO jpe@insaco.com.
→ Learn more about INSACO materials and capabilities.
New aero and defense PEKK-based FDM polymers from Stratasys
 Stratasys has partnered with top aerospace and defense companies to develop two newly qualified materials for 3D printing. Antero 800NA is a PEKK-based FDM polymer with excellent physical and mechanical properties for demanding applications. Antero 840CN03 is a high-performance PEKK-based FDM polymer with electrostatic dissipative (ESD) properties. These new advanced industrial solution materials were rigorously qualified in collaboration with Northrop Grumman, Boeing, Blue Origin, Raytheon, Naval Air Systems Command, the National Institute for Aviation Research, United States Air Force, BAE, and Stratasys Direct Manufacturing.
Stratasys has partnered with top aerospace and defense companies to develop two newly qualified materials for 3D printing. Antero 800NA is a PEKK-based FDM polymer with excellent physical and mechanical properties for demanding applications. Antero 840CN03 is a high-performance PEKK-based FDM polymer with electrostatic dissipative (ESD) properties. These new advanced industrial solution materials were rigorously qualified in collaboration with Northrop Grumman, Boeing, Blue Origin, Raytheon, Naval Air Systems Command, the National Institute for Aviation Research, United States Air Force, BAE, and Stratasys Direct Manufacturing.
Learn more.
EOS expands its Nickel superalloys for 3D printing
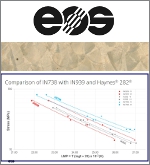 EOS, a leading supplier of manufacturing solutions for industrial 3D printing, has added two new metal additive manufacturing materials: EOS NickelAlloy IN738 and EOS NickelAlloy K500, both delivering excellent performance, part properties, and value to a variety of industries that leverage EOS Laser Powder Bed Fusion (LBPF) 3D-printing technology. The IN738 superalloy is aimed at high-strength, high-stress energy and turbomachinery applications, while the K500 superalloy is a cost-effective, corrosion-resistant option for chemical, maritime, and space industries.
EOS, a leading supplier of manufacturing solutions for industrial 3D printing, has added two new metal additive manufacturing materials: EOS NickelAlloy IN738 and EOS NickelAlloy K500, both delivering excellent performance, part properties, and value to a variety of industries that leverage EOS Laser Powder Bed Fusion (LBPF) 3D-printing technology. The IN738 superalloy is aimed at high-strength, high-stress energy and turbomachinery applications, while the K500 superalloy is a cost-effective, corrosion-resistant option for chemical, maritime, and space industries.
Learn more.
CNC machining: How to avoid high costs on thin walls
 Parts that are light and strong are crucial to nearly every industry. To achieve better performance without risking part failure, parts must maintain a specific wall-height-to-thickness ratio and wall-height-to-length ratio. Additionally, some geometries and supports can support thin walls to achieve a lighter component weight. Dive deeper into the cost drivers behind CNC-machined thin walls in this Xometry design-for-manufacturing article.
Parts that are light and strong are crucial to nearly every industry. To achieve better performance without risking part failure, parts must maintain a specific wall-height-to-thickness ratio and wall-height-to-length ratio. Additionally, some geometries and supports can support thin walls to achieve a lighter component weight. Dive deeper into the cost drivers behind CNC-machined thin walls in this Xometry design-for-manufacturing article.
Read the full article.
Eco-friendly thermoplastic: Light, rigid, strong, damping
 Polyplastics has launched PLASTRON® LFT (Long Fiber-Reinforced Thermoplastic) RA627P, an eco-friendly composite of polypropylene (PP) resin and long cellulose fiber that delivers low density, high specific rigidity, high impact strength, and excellent damping for a range of applications including audio components and housings of industrial components. LFT exhibits 10% lower density than 30% short glass fiber-reinforced PP resin, roughly the same flexural modulus, and a specific rigidity that is higher.
Polyplastics has launched PLASTRON® LFT (Long Fiber-Reinforced Thermoplastic) RA627P, an eco-friendly composite of polypropylene (PP) resin and long cellulose fiber that delivers low density, high specific rigidity, high impact strength, and excellent damping for a range of applications including audio components and housings of industrial components. LFT exhibits 10% lower density than 30% short glass fiber-reinforced PP resin, roughly the same flexural modulus, and a specific rigidity that is higher.
Learn more.
Sound-dampening foam with an eco edge
 BASF has introduced Basotect® EcoBalanced melamine foam, a material that helps to reduce the product carbon footprint (PCF) of many sound-absorption applications in the transportation, building, and construction industries. This easy, drop-in solution has an up to 50% lower PCF than the respective BASF standard grades but demonstrates the same material performance. Applications include engine covers, wall and ceiling sound absorbers, HVAC parts, and air cleaners.
BASF has introduced Basotect® EcoBalanced melamine foam, a material that helps to reduce the product carbon footprint (PCF) of many sound-absorption applications in the transportation, building, and construction industries. This easy, drop-in solution has an up to 50% lower PCF than the respective BASF standard grades but demonstrates the same material performance. Applications include engine covers, wall and ceiling sound absorbers, HVAC parts, and air cleaners.
Learn more.
Fastest large-format SLA 3D printer in the world
 Built on Formlabs' next-generation Low Force Display print engine, the new Form 4L SLA 3D printer delivers unmatched reliability with a 99% print success rate compared to other SLA 3D printers. These benefits, combined with a build volume nearly 5x the size of Form 4, allow Form 4L users to solve big problems and print smaller parts at high volume. Large-scale prints finished in under six hours.
Built on Formlabs' next-generation Low Force Display print engine, the new Form 4L SLA 3D printer delivers unmatched reliability with a 99% print success rate compared to other SLA 3D printers. These benefits, combined with a build volume nearly 5x the size of Form 4, allow Form 4L users to solve big problems and print smaller parts at high volume. Large-scale prints finished in under six hours.
Learn more.
Keypad teardown and design insights with Autodesk and Xometry
 Take a deep dive into the second revision of the macro keypad developed for Autodesk University's Factory Experience 2024 in this exclusive, on-demand webinar hosted by Xometry's Greg Paulsen and Autodesk Fusion's Jonathan Odom. This presentation features a live teardown of the keypad, showcasing how the design team addressed challenges and elevated the product. No registration required.
Take a deep dive into the second revision of the macro keypad developed for Autodesk University's Factory Experience 2024 in this exclusive, on-demand webinar hosted by Xometry's Greg Paulsen and Autodesk Fusion's Jonathan Odom. This presentation features a live teardown of the keypad, showcasing how the design team addressed challenges and elevated the product. No registration required.
Watch this Xometry webinar at your convenience.
Tube cutting and bending design guide: Xometry
 Xometry's no-cost tube design guide offers design tips and tricks for laser-cut tube parts, including: minimums, tolerances, and sizes. The guide also covers important rules for mandrel tube bending, such as tolerancing, distance between bends, bend center line radius, types of bends to avoid, and more. Incredibly handy. If you need parts, Xometry can help with that too. It's easy to get a quote.
Xometry's no-cost tube design guide offers design tips and tricks for laser-cut tube parts, including: minimums, tolerances, and sizes. The guide also covers important rules for mandrel tube bending, such as tolerancing, distance between bends, bend center line radius, types of bends to avoid, and more. Incredibly handy. If you need parts, Xometry can help with that too. It's easy to get a quote.
Learn more.
SPEE3D develops ultra-corrosion-resistant alloy
-- a game-changer for maritime additive manufacturing
 Australian manufacturer SPEE3D has developed two grades of an ultra-corrosion-resistant Nickel Aluminum Bronze alloy that are compatible with its Cold Spray Additive Manufacturing technology. The powder material is a game-changer for maritime OEMs and the U.S. Navy, as it will help with supply chain delays and keep critical maritime systems operational.
Australian manufacturer SPEE3D has developed two grades of an ultra-corrosion-resistant Nickel Aluminum Bronze alloy that are compatible with its Cold Spray Additive Manufacturing technology. The powder material is a game-changer for maritime OEMs and the U.S. Navy, as it will help with supply chain delays and keep critical maritime systems operational.
Read the full article.
New polymer bearings are PFAS- and PTFE-free
 igus has developed a new polymer bearing material called iglide JPF that is free of both per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) and polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE). This innovation marks an important step in the company's efforts to create sustainable alternatives to conventional plain bearings. JPF is a dry-running, wear-resistant polymer that offers comparable friction and wear performance to iglide J. It delivers high wear resistance and durability.
igus has developed a new polymer bearing material called iglide JPF that is free of both per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) and polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE). This innovation marks an important step in the company's efforts to create sustainable alternatives to conventional plain bearings. JPF is a dry-running, wear-resistant polymer that offers comparable friction and wear performance to iglide J. It delivers high wear resistance and durability.
Learn more.
New high-speed PSLA 270 printer from 3D Systems
 The all-new PSLA 270 projector-based polymer 3D-printing platform and associated new materials from 3D Systems enable faster production times for a wide range of applications. This machine's high throughput and accuracy make it ideal for industries like healthcare, aerospace, automotive, and manufacturing, where precise and durable components are critical. Complementary Wash and Cure systems streamline post-processing and ensure high-quality finished parts.
The all-new PSLA 270 projector-based polymer 3D-printing platform and associated new materials from 3D Systems enable faster production times for a wide range of applications. This machine's high throughput and accuracy make it ideal for industries like healthcare, aerospace, automotive, and manufacturing, where precise and durable components are critical. Complementary Wash and Cure systems streamline post-processing and ensure high-quality finished parts.
Learn more including materials and build sizes.
Engage the spin rocket motor: Drop of U.S. mock B61-12 nuclear weapon is first of new flight tests

An F-16C makes a pass over Nevada's Tonopah Test Range after a March test of a mock nuclear weapon as part of a Sandia National Laboratories life extension program for the B61-12. Teams will spend months analyzing the data gathered from the test. [Photo: John Salois]
From a distance, the drop of a mock nuclear weapon -- containing only non-nuclear components -- was a mere puff of dust rising from a dry lake bed at Nevada's Tonopah Test Range. However, it marked the start of a new series of test flights vital to the nation's B61-12 weapon refurbishment program.
Initial data showed the March 14 test was a success, said officials at Sandia National Laboratories, which runs Tonopah. For months, teams will be analyzing a wealth of data they collected from this first of a qualification test series planned over the next three years.
Those watching from the tower of the range's Test Operations Center felt "excitement and pleasure that it all worked as we expected," said Anna Schauer, director of Sandia's Stockpile Resource Center.
The B61-12 consolidates and replaces four B61 variants in the nation's nuclear arsenal. The first production unit in the weapon's life-extension program is scheduled to be completed in 2020.

An F-16C from Nellis Air Force Base in Nevada releases a mock nuclear weapon for a March test at Tonopah Test Range. The test is the first in a series planned over the next three years. [Photo: James Galli]
Test day dawned cloudless and wind-free, perfect weather at the range, an area of 280 square miles with two main target areas on flat lake beds sitting between mountain ranges. Workers from Sandia and contractor Navarro Research and Engineering operated tracking telescopes, remote cameras, and other instruments in the field to gather information on the reliability, accuracy, and performance of the weapon under conditions meant to replicate operations.
An F-16C from Nellis Air Force Base near Las Vegas, chosen to drop the test unit representing a B61-12, began with a dry run over one of the lake beds. But during his next pass for the planned release, he had to roar off after a small group of wild horses ambled onto the lake bed.
A video feed from a remote camera in the area showed the horses trotting away to safety, herded by wranglers: security officers in a white pickup, its headlights and rack lights pulsing. "That's a first for us," said test director Joe Simile of Sandia. "We've never had to chase horses away from the target."
The extra pass meant the F-16 carrying the test unit and a companion wingman F-16 would have to refuel in flight from a tanker airplane circling the area before returning to base.
F-16 final pass: "Commence run"
Then, horses cleared off, the pilots circled back. The test director queried those responsible for the various aspects of the test, from telemetry to the pilot of the drop plane. One by one they gave the test a go and a disembodied voice over the intercom announced, "Range is green. Cleared to release."
The announcement, "Commence run," galvanized dozens of people watching and listening to live feeds of preparations at the tower. Most dashed out to the balconies to watch -- a natural reaction despite knowing the lake bed was miles away and they'd see nothing more than dust rising from the high-altitude drop. The video feed, a much closer look, showed the F-16 release the test unit, the unit's spin rocket motor ignite, and the mock weapon fall through the air.
"It's great to see things all come together: the weapon design, the test preparation, the aircraft, the range, and the people who made it happen," Schauer said.
The U.S. Department of Energy's website says, "In April 2003, the Nuclear Weapons Council Standing and Safety Committee (NWCSSC) approved the development of a new Spin Rocket Motor based on Sandia's assertions that test data collected between 1997 and 2002 showed the motors, due in large part to 'detrimental aging,' were not performing according to specifications. Detrimental aging occurs when a component's age prevents it from performing to meet military requirements."
According to a May 18, 2014, article in the Albuquerque Journal, "Spin motion is needed to stabilize the bomb as it glides toward its target. It's controlled by rocket motors and slanted fin tails. But in earlier B61 designs, air plumes from the motors have interfered with fin performance, thus weakening the push, or torque, created by the motors and reducing spin rates."
The article also says a new tail kit assembly "is important because it adds a guidance system to the bomb, basically converting it from a gravity-dependent dumb bomb into a smart one that can be aimed more precisely at a target."
These are only two of many steps taken in the broad nuclear arsenal modernization project.
"The bomb modernization program, which aims to extend the B61's life another 20 years, is one of the biggest endeavors undertaken at Sandia since before the Cold War ended," the Albuquerque Journal article states.
Hans Kristensen, a nuclear weapons analyst at the Federation of American Scientists in Washington, D.C., said in the Albuquerque Journal article, "The National Nuclear Security Administration estimated about $4 billion originally in 2010, and then in 2012 that ballooned to $8 billion. The new tail kit assembly alone could cost up to $1.5 billion."
"The U.S. Department of Defense now estimates total B61-12 program costs at $10.4 billion," the article said, attributing that estimate to Kristensen. "With about 400 B61 bombs to be refurbished, that's about $25 million per bomb."
VIDEO: Tonopah Test Range flight test.
After the drop, the two F-16s turned to scream past the control tower about a half mile away, giving observers a closer look at the planes.
On the lake bed, the only sign of the drop was a surprisingly neat hole. An hour or so after the test, Simile stood near the hole, describing plans to recover the weapon, his discussion punctuated by a warning beep-beep-beep from a truck backing up to unload recovery equipment.
Crews were back later to dig the mock weapon out of the dirt.
"The test unit recovery went very well, with the unit packaged up for return to Albuquerque," said Lee Post, B61-12 flight test lead. "We can only hope our future tests go this well."
Source: Sandia National Laboratories
Published April 2017
Rate this article
View our terms of use and privacy policy
